Despite the amount of traffic we may attract to our sites, or even the amount of non-monetary conversations we acquire, we may be left wondering: Why aren’t people buying my products? It’s disheartening to see low sales and site traffic with no obvious reason as to why. In order to identify possible roadblocks for customers on our site, we need to take a step back and explore our website from the perspective of our customers.

It may sound cliché, but putting yourself into the shoes of your potential customers is key to creating a site that converts. From the language you are using to the structure of your site, keeping your target customer in mind aids in making a site that is compelling and easy to use. When concerned about low conversations and sales, take into consideration the following questions:
Is it easy to find your products & services?
The first step towards conversions is getting users onto your site. If you were to search for terms related to your products and services on Google, what comes up? Making sure that your SEO strategy is successfully bringing users to your site is important to keep track of. Searching for your site on search engines, analyzing traffic data, and focusing on keywords that your customers use to search for the products and services you offer can help bring more traffic to your site.
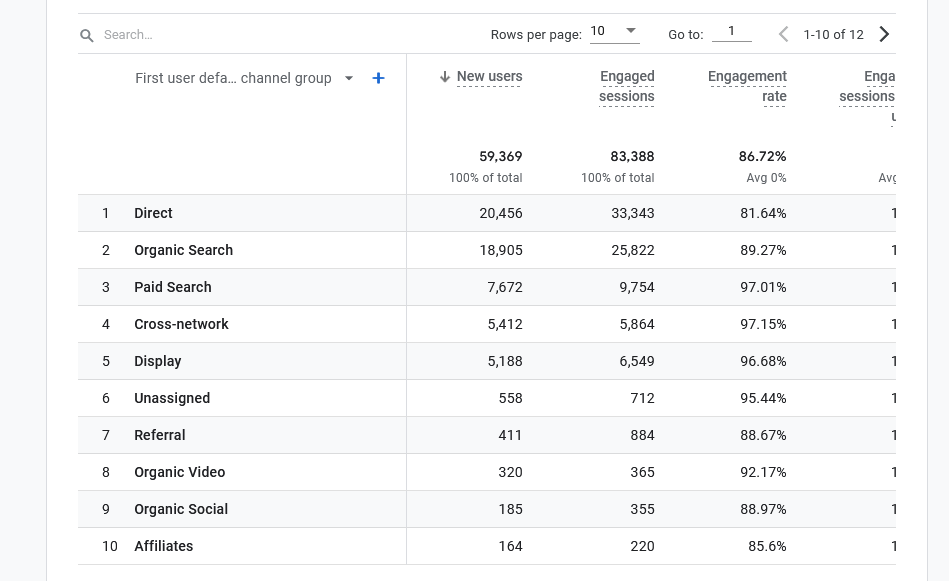
Beyond users finding your business on Google, you should also consider how easy it is to find your products and services on your site. How intuitive is the structure of your website? Optimizing your navigation bar and call-to-actions for ease of use and understanding is key to successfully guide users to your sales pages. Have a friend explore your site or check out user data concerning the journey users take through your site via the GA4’s Explore options to identify possible missteps in your site’s guidance.
Another potential roadblock to getting users to see what you have to offer is the mechanical performance of your site. How does your site feel? Slow and unresponsive user experiences, page crashes, buggy interfaces, and lack of cross device optimization can make it difficult to traverse your site, pushing potential customers away. Keep a look out for broken pages and links, as well as optimize your site for mobile use and speed.
Is the “why” of your products clear and compelling?
Once a user is on your site, you only have a handful of time to pique their interest, so its important to be straight to the point. Why should they consider your products? Within your landing page, it should be clear what your selling, who your products are for, and why people should by them. Making sure that our above the fold content and sales pitches are compelling and attractive to our target audience is important to getting users to even consider buying from our businesses.
On top of illustrating why users should consider our products, the language we use to describe our offers can impact whether a user wants to become our customer. Beyond just explaining why our products are good and can help potential customers, we must also ask ourselves: Why should they buy your services now? Creating a sense of urgency pushes customers to consider your offerings more seriously. This urgency doesn’t have to aggressive, such as a time limited offer, but instead can be an attractive vision of what buying our services will be like. Through our content and through customer testimonials, we can illustrate just how well our products resolve our customers’ pain points, making our services tangible and their value clear.
Can users trust your products & services?
Even if your site is visually stunning and easy to use, another aspect of turning visitors into customers I gaining their trust. Why should new customers trust your company? For users who are new to your business, hesitancy may stop them from considering buying from you. To avoid losing hesitant customers, it’s important to make sure that your content clearly shows your credentials and success. You can share your company story or statistics that show how good your company is doing. You can also share customer testimonials and ratings so that potential customers can see that real people have found happiness in your services.
Another aspect of trust to consider is clearly sharing the “small text” of buying your products. Are there any hidden fees or policies that customers may not know? Being transparent with your users about taxes, delivery charges, privacy policies, and so forth creates a sense of professionalism and sets expectations ahead of time. Users want to know what buying your products entails ahead of time rather than being blindsided by surprise details during the buying process. Having features such as estimated taxes alongside easy access to your privacy and shipping policies can help users trust your business.
Is it easy to understand what your products & services are?
Whether you sell physical products or intangible services, selling online can make it hard for users to understand what you are offering. Are your product pages painting a complete picture? Taking a look at your individual product descriptions or service tier lists, consider what information may be missing or even confusing to users. Part of building a successful product description is using language that our customers will understand so that we can make the product tangible despite being online. With services, consider how easy it is to understand how your service works. Taking the user step by step through your service, such as through infographics, can help users get a better picture of what they are buying.
Is it easy to buy your products & services?
Once your potential customer has decided to go ahead and buy your products and services, all that’s left is to go through the checkout process. Is your checkout process easy to go through? When it’s time to buy your products, the experience should be easy and intuitive. Complex forms, excessive required information, mandatory account creation, and so forth can cause a potential customer to back out at the last minute. Keep your checkout process short and offer features such as guest check out and auto fill to make the buying process a pleasant, easy experience.
Want to learn more?
Optimizing our sites for conversions is a continuous process. Customer expectations change and technology evolves, making it important to keep tracking our successes and improving our sites. Check out our blog for more advice on making your website better. If you want more hands-on guidance for improving your website, join the waitlist for Carrie Saunders’ upcoming course, “The Converting Website.” In this course, she will dive into a variety of important factors that aim to optimize your website.